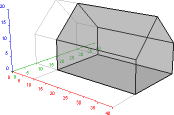
The X and Y-axes generally correspond to dimensions of length and width while the Z-axis corresponds to that of height as indicated in the diagram at right.
Distances are given in a triplet of dimensions written as (X,Y,Z). As defined (noting it is dependent on view angle as in the view at right), the X-axis is oriented left-to-right, the Y-axis is oriented top-to-bottom, and the Z-axis is oriented up-to-down (or in and out of the plane of the screen).
Visual assumes a Z-dimension of zero if coordinates are specified as a couplet (X,Y).
Positive dimensions are to the right, toward the top, and up or out of the screen. Conversely, negative dimensions are to the left, toward the bottom, and out of the screen.
Isometric views that are from an angled vantage point are labeled like a compass. In the example to the right, the diagram is viewed from the NE direction.

The origin (0,0,0) is not labeled in Visual and it is not necessary to construct objects starting at the origin. Objects can be placed anywhere in the model space.
An Axis can be drawn for reference in the Design Environment as is shown at right for all three axes, noting that the color of each axis has been changed to coordinate to the axis colors used in Visual.
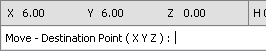
Absolute Coordinates are those that are specified and entered with reference to the origin (0,0,0). These coordinates are displayed in black in the top of the Status Bar. Visual displays the coordinates of the cursor in this part of the Status Bar at all times. Absolute Coordinates can be displayed at/with the mouse crosshairs, see Environment Settings.
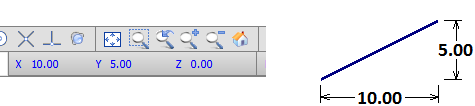
Relative Coordinates are displayed in the Status Bar while in a command. The origin for Relative Coordinates is the initial point of user input. For example, Visual will display an (X,Y,Z) of (10,5,0) in the blue coordinates on the bottom of the Status bar if the mouse is moved 10 units to the left (+X) and 5 units up (+Y). The Z-dimension is 0 because the drawing is assumed to be done in a plane unless user input changes that. Relative Coordinates can be displayed with the mouse crosshairs, see Environment Settings.
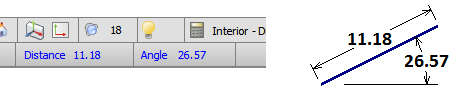
As an additional part of Relative Coordinates, Visual displays the polar coordinates as a length and an angle. These reference a line created by extending from the first (or last) selection point made in the command to the current mouse position. The angle shown is between this same line and the X-axis. The "line" may be imaginary depending on the command executed; e.g. when drawing a rectangle.